Functional Abdominal (Tummy) Pain
This page has been developed for parents and carers of children who have been diagnosed with Functional Abdominal Pain. If your child has not been diagnosed with Functional Abdominal Pain, please visit our pages on Recurrent Abdominal Pain or Tummy Pain. If you are concerned about your child's tummy pain please contact your healthcare provider.
What causes functional abdominal pain?
Although the condition has been extensively studied, we are still unsure of the exact cause. It does seem that in some children, the nerves in their gut become very sensitive and pain is experienced even though the intestines are functioning normally.
The gut and the brain communicate to regulate health and disease through a connection called the brain-gut axis.
We all need a healthy and diverse combination of bacteria in our gut, known as gut flora. Sometimes after a mild illness, this important balance can be disturbed, leading to hypersensitivity of the bowel wall.
Triggers that don’t normally cause pain such as stretching or bloating can trigger a pain signal to be sent to the brain if the bowel wall is sensitive.
Often the brain will recognise that this is just a normal stretching sensation, and send a message back to the bowel which turns off the pain signal by closing the pain gate.
Sometimes, when children feel worried it can prevent these pain signals from getting filtered out and the pain gate stays open. So when the bowel has the sensation of stretching, a pain signal is sent to the brain and the child feels abdominal pain.
1. A part of the bowel is stimulated in a painful way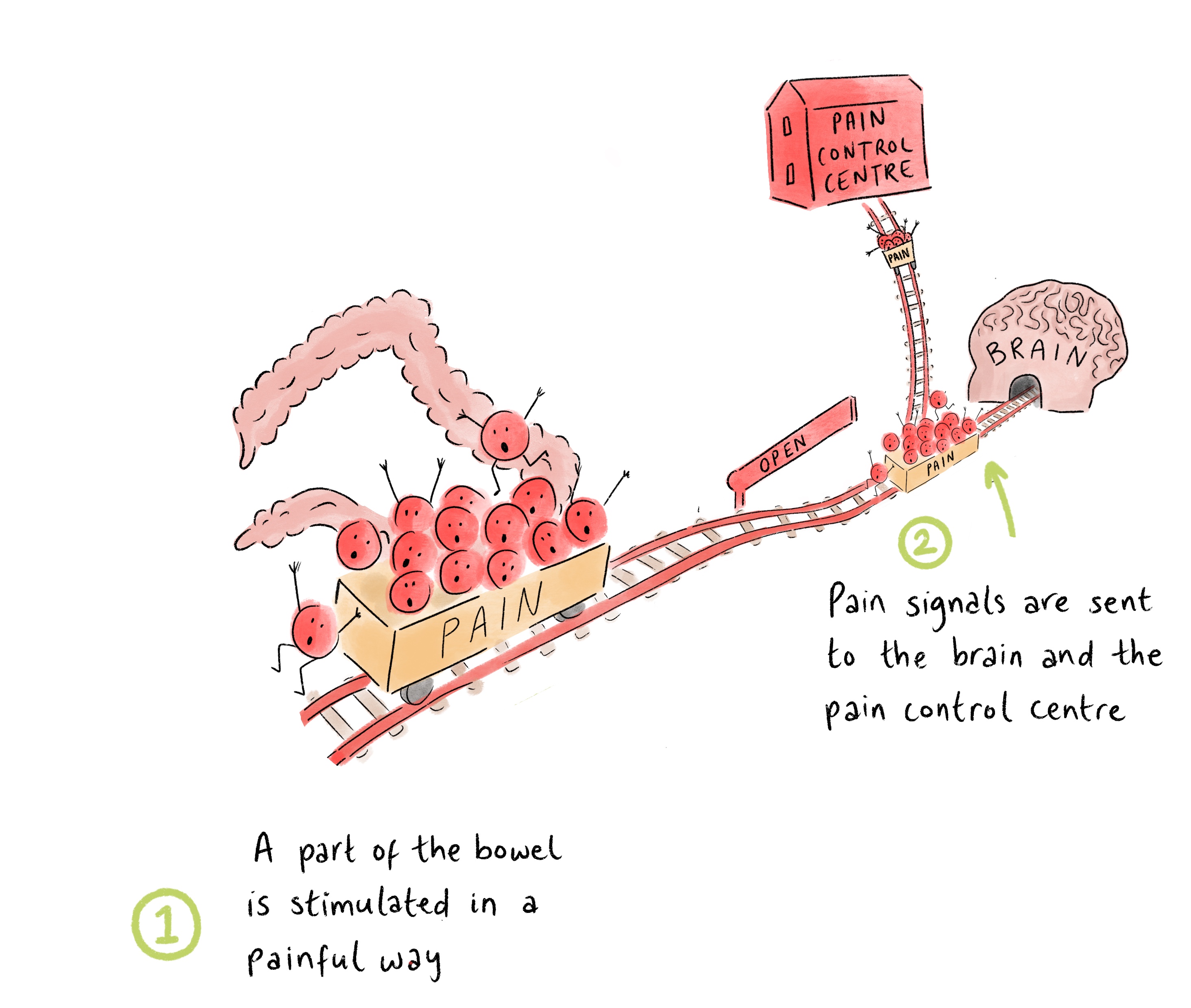
2. Pain signals are sent to the brain and the pain control centre
3. The neuromatrix connects lots of parts of the brain together. 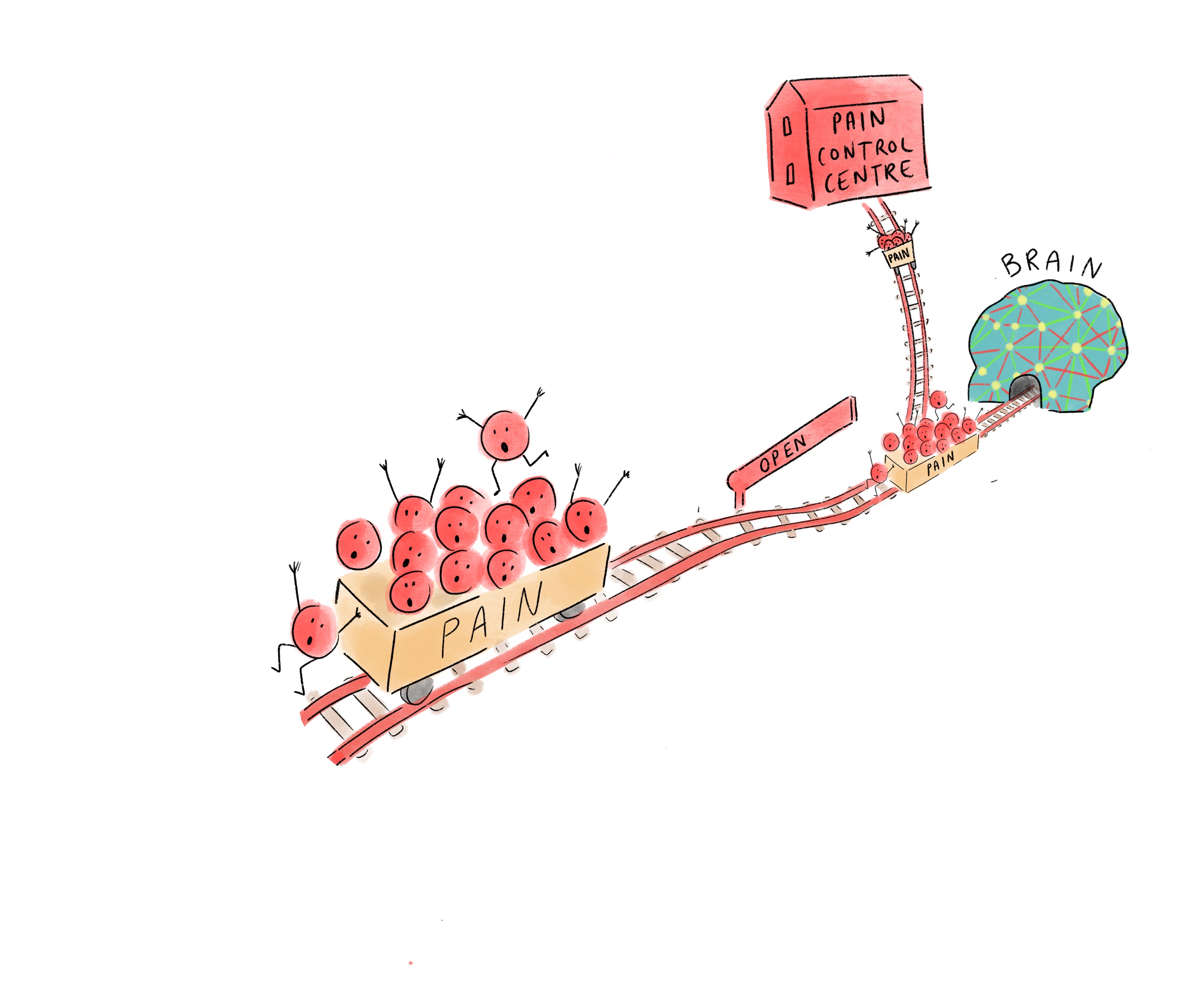
Thoughts, emotions and sensations come together to create an experience of pain
4. Messages from the brain influence the pain control centre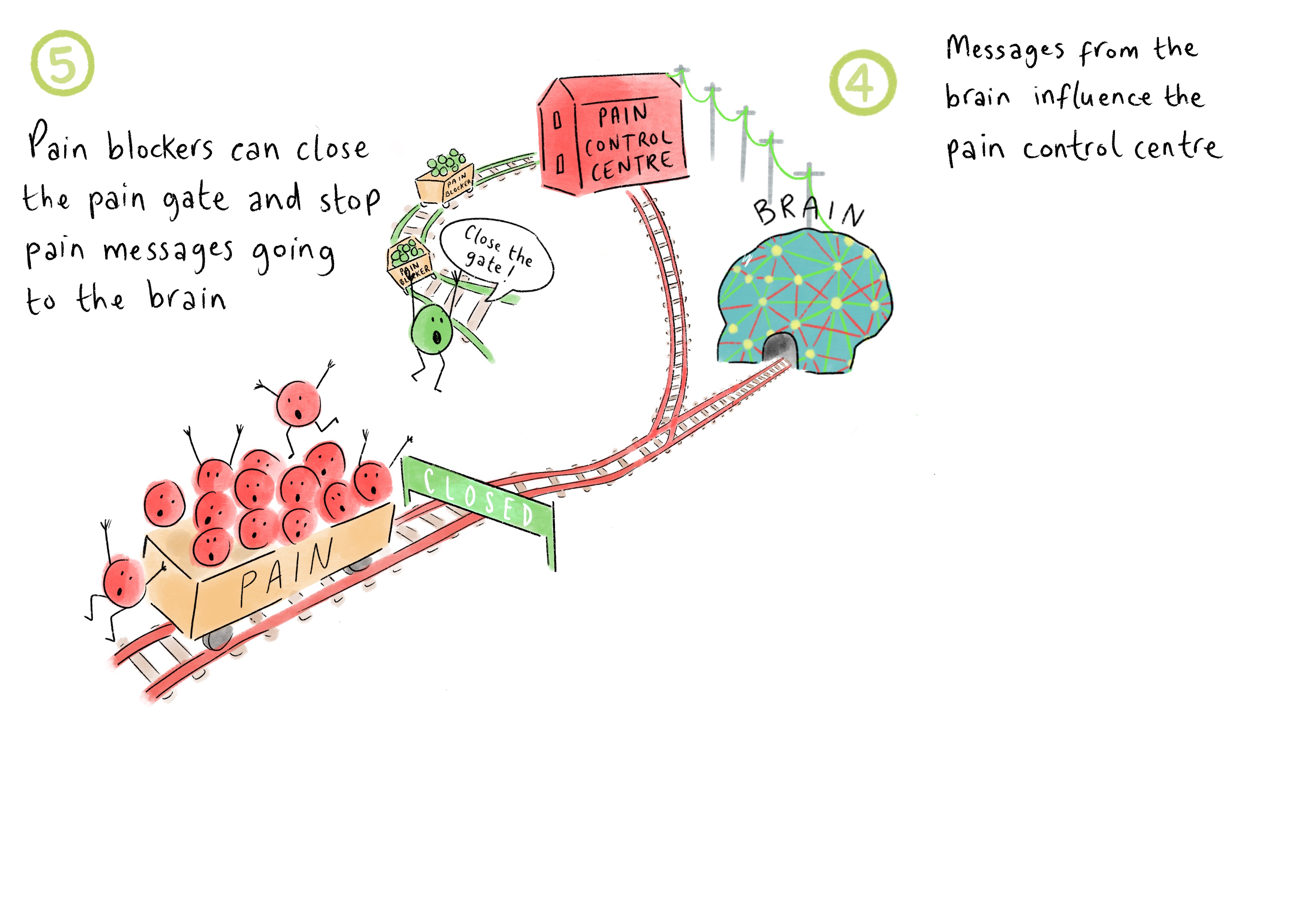
5. Pain blockers can close the pain gate and stop pain messages going to the brain
6. Worrying thoughts and low mood can change messages going to the pain control centre.
7. Pain blocking messages stop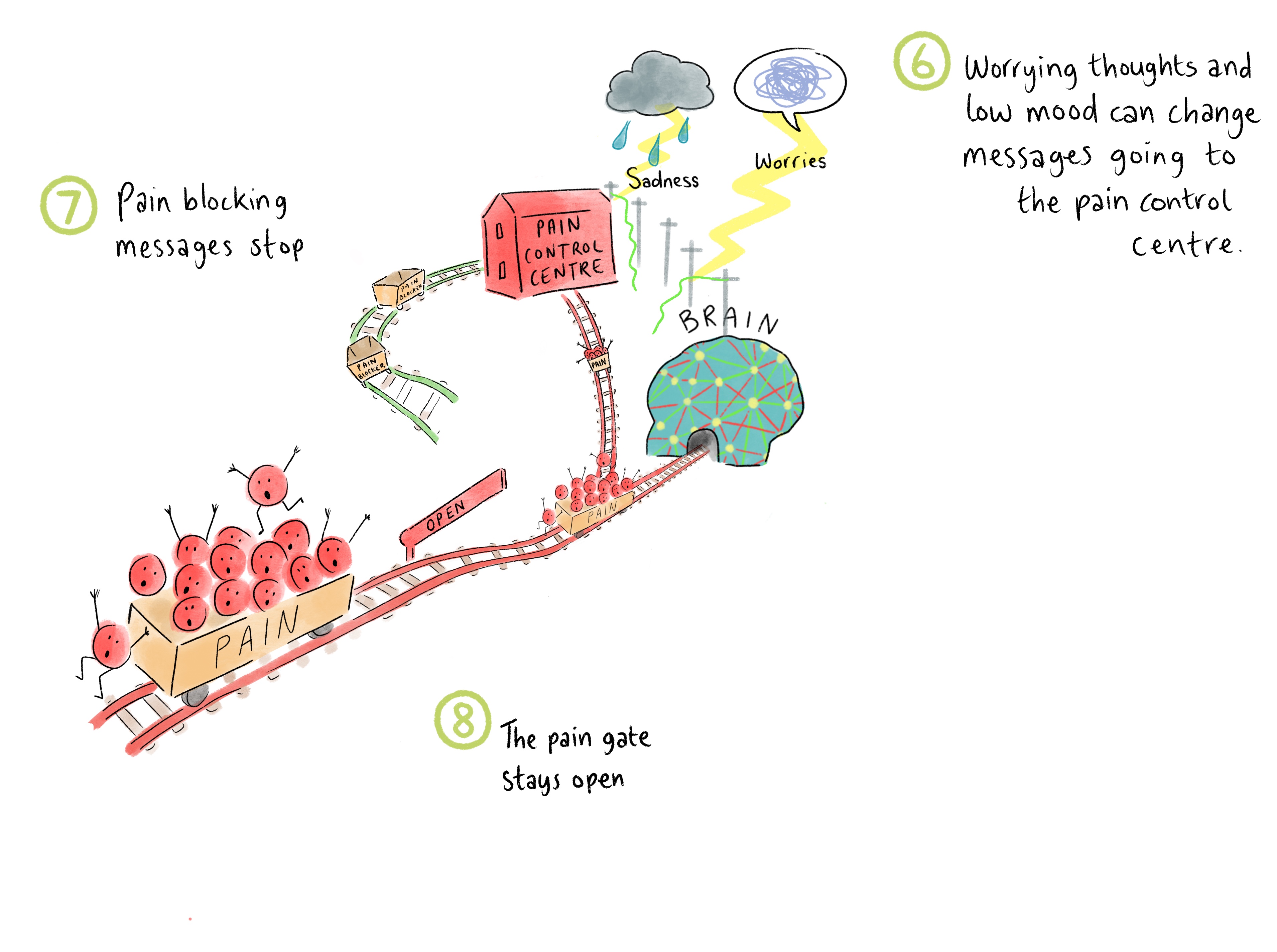
8. The pain gate stays open
9. The sensation of deep touch can close the pain gate and stop pain messages going to the brain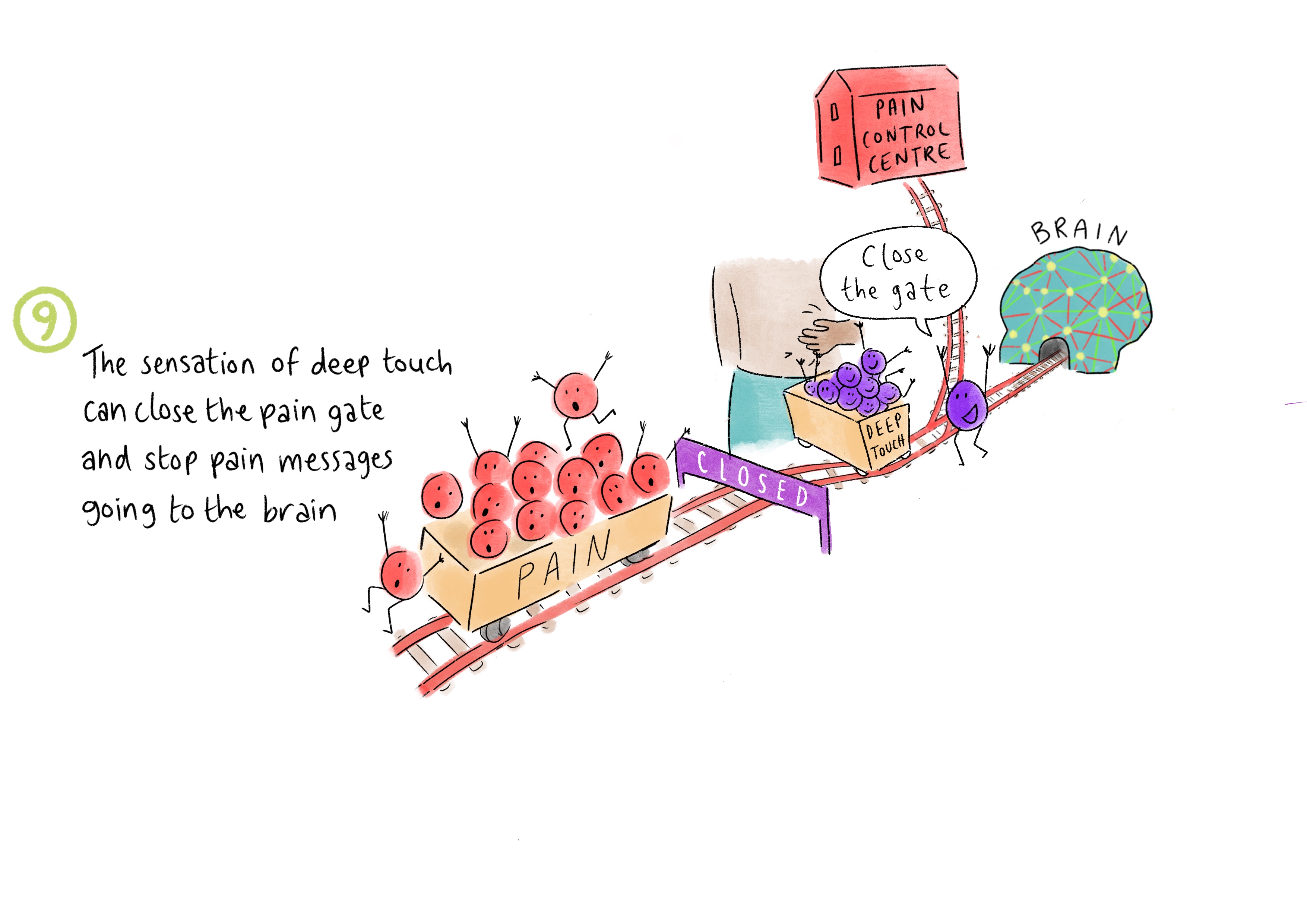
10. Lots of things can help reduce the brain’s sensitivity to pain
11. Pain blocking messages are sent to the pain gate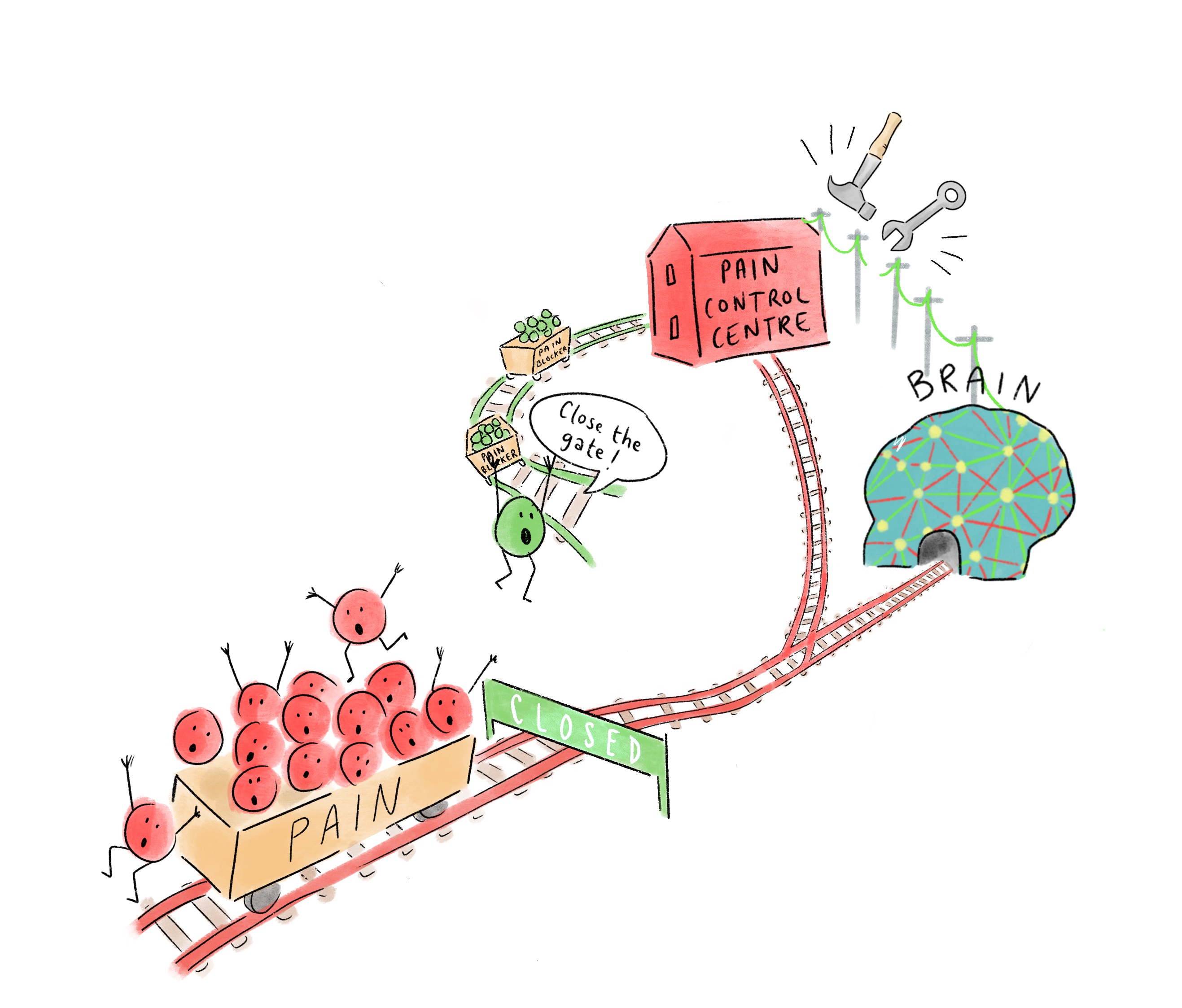
12. The pain gate closes
What treatment is available for functional abdominal pain?
- This condition takes time to manage and you may need more than one appointment with your doctor. Your GP practice may refer your child to secondary care (paediatrics). There is not enough evidence of a specific treatment or intervention being useful. A large part of management involves discussion, explanation and reassurance rather than treatment or intervention.
- It is important that you and your child understand there is no physical abnormality which is causing their pain. Anxiety about a possible underlying disease, or focusing on the pain, will make it worse. This does not mean you should ignore the condition, but to offer reassurance and distraction rather than reinforce it.
- For a younger child, it may be helpful to explain to them that their tummy is very sensitive and sometimes hurts as the food goes around the bends.
- An older child may be able to understand the information about what causes functional abdominal pain.
- It is important that you do not allow the condition to change your child’s social activities or allow it to become a reason for missing school. Even when the pain persists, it is reassuring to learn that this is a known condition, and that it is not dangerous. Being positive about getting better will send the right message to your child.
- Mindfulness activities can be helpful for some children.


