My baby has Fever / High Temperature
Fever in babies less than 3 months of age is much more likely to be due to a serious infection requiring urgent treatment compared to fever in an older child. For this reason, all children under 3 months of age with a temperature above 38°C / 100.4°F should be urgently reviewed by a healthcare professional. The only exception is if they have a fever in the 48 hours following their first set of vaccines (given at 8 weeks of age) – in this situation, it is OK to give them paracetamol without seeking medical advice if your baby is otherwise well.
How to take your baby’s temperature:
You should measure your baby’s temperature under their armpit. Hold their arm against their body to keep the thermometer in place for however long it says in the manufacturer's instructions – usually about 15 seconds; some digital thermometers beep when they're ready. You should not measure their temperature on the forehead or in their ear – it will not be accurate in young children.
When should you worry?
If your baby has any of the following:
- Becomes pale, mottled and feels abnormally cold to touch
- Is going blue around the lips
- Severe breathing difficulty - too breathless to talk or eat/drink
- Has a fit/ seizure
- Becomes extremely agitated (crying inconsolably despite distraction), confused or very lethargic (difficult to wake)
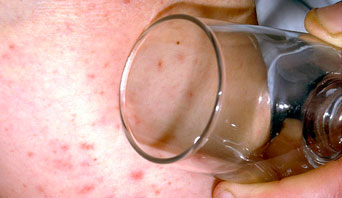
- Develops a rash that does not disappear with pressure (the ‘Glass Test’)
- Is under 3 months of age with a temperature of 38°C / 100.4°F or above (unless fever in the 48 hours following vaccinations and no other red or amber features)
You need urgent help
Go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department or phone 999
If your baby has any of the following:
- Is finding it hard to breath
- Seems dehydrated (sunken eyes, drowsy or not passed urine for 12 hours)
- Is becoming drowsy (excessively sleepy) or irritable (unable to settle them with toys, TV, food or picking up) – especially if they remain drowsy or irritable despite their fever coming down
- Has extreme shivering
- Is 3-6 months of age with a temperature of 39°C / 102.2°F or above (but fever is common in babies up to 2 days after they receive vaccinations)
- Is getting worse or if you are worried
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today
Please ring your GP surgery or call NHS 111 - dial 111
If none of the above features are present
Additional advice is also available for families to help cope with crying in otherwise well babies.
Self care
Continue providing your child’s care at home. If you are still concerned about your child, call NHS 111 – dial 111
What should you do?
To make your baby more comfortable, you may want to lower their temperature using liquid paracetamol (e.g. calpol/other brands). This should be given only on the advice of a health professional as most babies under 3 months of age with fever will need medical attention.
Do not give more than the maximum recommended daily dose of medicine. However, remember that fever is a normal response that may help the body to fight infection and paracetamol will not get rid of it entirely. Medicines are helpful in reducing the discomfort associated with fever.
Avoid sponging your baby with tepid water – it doesn’t actually reduce your baby's temperature and may cause hypothermia ( Low body temperature). Babies with fever should not be underdressed or overwrapped.
Encourage them to drink plenty of feeds.
If a rash appears, do the glass test.
Where should you seek help?
- If it is non-urgent, speak to your local pharmacist or health visitor.
- If your child has any of the above features, urgently contact your GP surgery. For an urgent out-of-hours GP appointment, call NHS 111.
- You should only call 999 or go your nearest A&E department in critical or life threatening situations.
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as loss of consciousness, suspected heart attacks, breathing difficulties, or severe bleeding that cannot be stopped. If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.


